How to Compost PLA?
Industrial Composting Process, Chemical Stages and
Recommendations to Consumers:
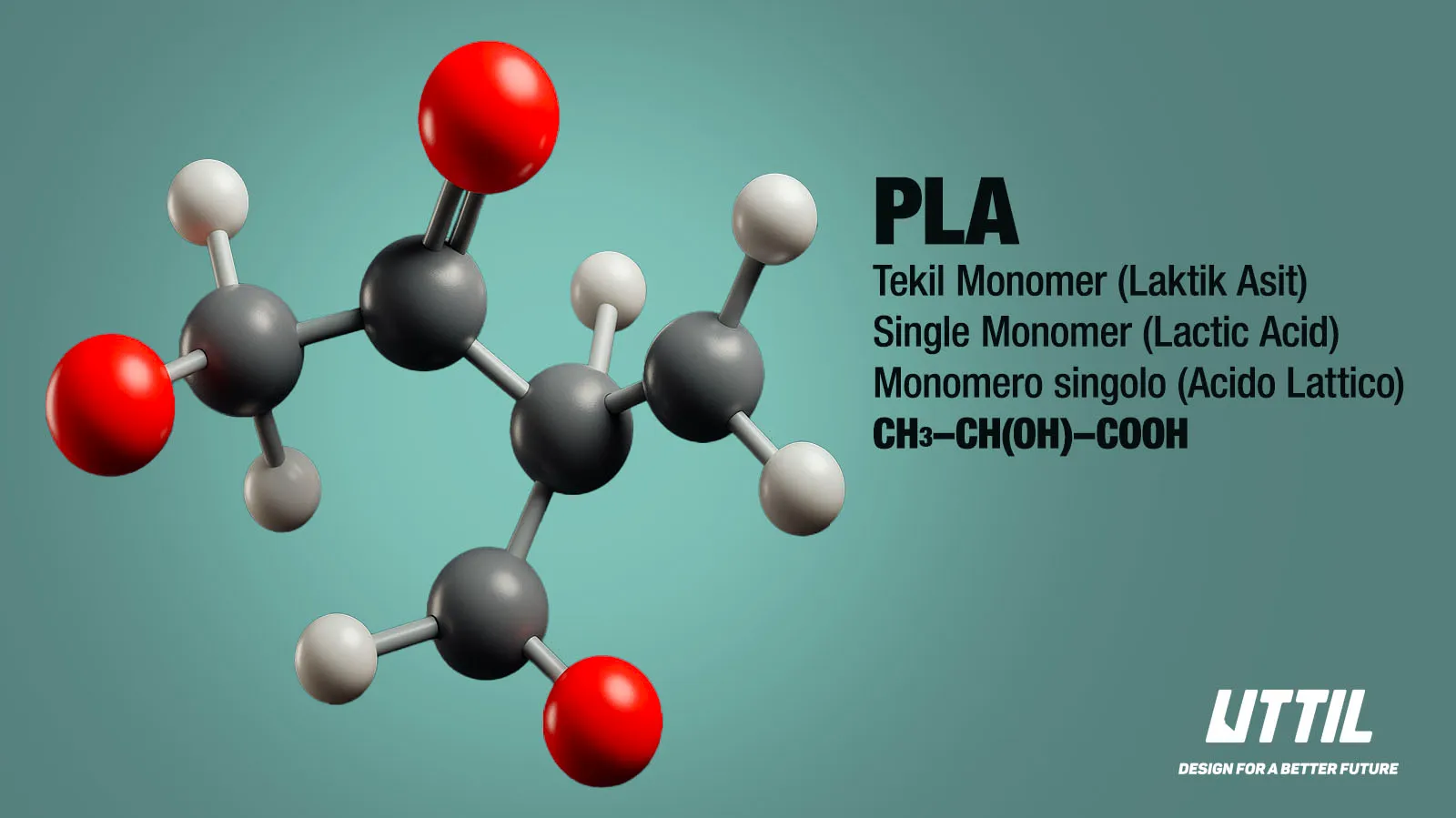
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a
biobased thermoplastic derived from renewable resources, such as corn starch
and sugarcane. PLA, which is used in various applications such as packaging,
disposable products, and 3D printing, is environmentally friendly; however, it
is necessary to closely examine the composting process to understand its
environmental impact fully.
In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of
the industrial composting process for PLA, including the chemicals involved,
its environmental impact, EU standards, and specific recommendations for
consumers.
Is PLA Really Compostable?
In short: Yes,
but only under controlled industrial conditions.
Because PLA does not degrade in the compost bin at home
or when left in nature:
Its crystal structure is organised; it requires high
temperature, humidity and oxygen; it takes time to break down into chains of
molecules that microorganisms can break down in the natural environment.
Industrial Composting Process:
How PLA Degrades
Industrial composting plants are controlled systems that
provide the high temperature and humidity required for the breakdown of PLA.
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Temperature |
58 ± 2 °C |
|
Nem |
%50-60 |
|
Oxygen level |
≥ %18 |
|
Duration |
60-90 days |
|
pH |
6.0-7.5 (neutral) |
Composting Stages:
|
Phase |
Duration |
Process |
Conclusion |
|
Hydrolysis |
0-10 days |
PLA molecular chains are broken down by heat and
moisture. |
Small
molecules such as lactic acid and lactide are formed. |
|
Biodegradation |
10-40 days |
Microorganisms metabolise lactic acid. |
CO₂, H₂O and biomass are formed. |
|
Stabilisation and maturation |
40-90 days |
The compost transforms into a soil-like structure. |
Odour and
acidity are stabilised, and safe organic matter is obtained. |
Chemicals arising in the process:
|
Chemical |
Source |
Effect / Usage |
|
Lactic Acid (C₃H₆O₃) |
Hydrolysis of PLA |
Carbon source for microorganisms |
|
CO₂ |
Breakdown of lactic acid |
Released during composting |
|
Water (H₂O) |
Metabolism by-product |
Provides moisture balance |
|
Microbial biomass |
Proliferation of microorganisms |
Structural component of the final compost |
No toxic substances are formed in this
process. PLA does not contain BPA, phthalates or heavy metals.
European Union Compostability
Standard: EN 13432
In Europe, a product must meet the EN 13432 standard
to be considered compostable. This standard includes the following
requirements:
|
Criteria |
Necessity |
|
Biodegradability |
90+% conversion to CO₂ within 180 days |
|
Degradability |
At 12 weeks, more than 90% should be fragmented ≤2
mm |
|
Toxicity testing |
Compost must not inhibit plant growth |
|
Heavy metal limit |
Metals such as lead, cadmium below certain limits |
A PLA product without EN 13432 certification is
not considered "compostable".
Recommendations for Consumers
When
using products containing PLA, the following points should be noted:
Check the certificate:
Do
not compost products that are not labelled EN 13432, OK compost
INDUSTRIAL or TÜV Austria HOME. All PLA products offered by
UTTIL are produced with raw materials labelled "TÜV Austria, OK compost
INDUSTRIAL".
Do not recycle, PLA products
should be disposed of in the organic waste bin:
If
PLA is mixed with plastics such as PET, it disrupts the recycling system. PLA
products should be disposed of in the organic waste bin, not recycled.
Do not dispose of in home
compost (usually):
Standard
PLA does not degrade in home compost. If you wish to compost it at home, the
product must be labelled "home compostable".
Is it Possible to Compost PLA
at Home?
It
is not easy,, but technically possible. Here are some tips for successful home
PLA composting:
|
Application |
Description |
|
High temperature |
Target ≥50 °C per day (hot composting technique) |
|
Shredding |
The PLA pieces should be cut into small pieces or
ground into chips. |
|
Pre-treatment |
PLA can be kept in boiling water for 1-2 hours to
initiate hydrolysis. |
|
Humidity control |
Maintain humidity between 50-60 per cent. |
|
Compost additive |
The microbial diversity can be increased by adding
manure, vermicompost, or mushrooms. |
|
Time |
PLA can take 6-12 months to dissolve in home
compost completely. |
However, this method is not completely reliable for
commercial PLA products. Products labelled "home compostable" have a
high probability of success.
Conclusion
PLA is a more sustainable option than traditional
plastics.
However, being compostable does not mean that it will
degrade in any environment.
The actual dissolution only takes place under industrial
composting conditions.
Certificates such as EN 13432 are vital indicators
to check that this process is working properly.
Making conscious choices as a consumer makes a
significant difference in reducing the impact of not only PLA but also all
bioplastics on the environment.
Sources:
European Bioplastics Association -
https://www.european-bioplastics.org
EN 13432:2000 -
Packaging: Requirements for Packaging Recoverable Through Composting and Biodegradation
ISO 17088 - Specifications for
Compostable Plastics
ASTM D6400 - Specification for
Labelling of Plastics Designed to be Aerobically Composted
NatureWorks LLC - PLA Industrial Composting Data Sheet